Overview
Within This Page
The Conference/Classroom space types are areas used for formal meeting, training, and teleconference activities. This space type does not include spaces requiring ceilings in excess of 12'-0"; (h); architectural features to accommodate projection systems using ribbon type cellulose acetate or other safety film used in conjunction with electric arc, xenon, or other light source projection equipment that develops hazardous gases, dust or radiation, or where cellulose nitrate film is utilized; food service preparation areas; special equipment such as rear projection screens; special electronics control and ADP spaces for audiovisual recording broadcasting, and computer-assisted meetings (classified as ADP space type); or special acoustical design including non-rectilinear spaces dictated by acoustical properties.


Space Attributes
The Conference/Classroom space type requires flexibility, durable finishes to anticipate maximum use, and integrated utility lines such as voice, data, and power to accommodate a variety of multimedia presentations and tele- and video- conferences. Typical features of Conference/Classroom space types include the list of applicable design objectives elements as outlined below. For a complete list and definitions of the design objectives within the context of whole building design, click on the titles below.
Accessible

Conference/Classroom space should be accessible and in an accessible location. An accessible floor plan is one in which people who use mobility devices (e.g., wheelchairs, scooters, walkers, crutches, canes) can maneuver throughout and use the amenities independently; people who are blind or have low vision can navigate easily and safely; people who are deaf or have hearing loss can use assistive listening systems and see speakers, interpreters, and captioning; and all participants feel comfortable and ready to be engaged in discussion. Furniture should be arranged to allow everyone to fully participate.
An accessible meeting presentation ensures that all participants have equal access to the meeting's content. Locations and spaces for auxiliary aids and services that bridge communication, between people who are deaf or have hearing loss and people who are hearing so that each can understand the other, should be provided. Assistance may include qualified sign language and oral interpreters, assistive listening systems, and realtime captioning (also called CART –– communication access realtime translation or computer–aided realtime translation) services. Accessible exchange of information for people who are blind or have low vision may require that printed materials are provided in alternate formats (e.g., Braille, large print, on CD) or that notetakers are provided.
Barriers to access within the conference/classroom space can be temporarily resolved by the use of ramps to reach stages, platforms, or podiums, and placing detectable objects in locations for the vision impaired to remove the hazards of any protruding objects.


Flexible furniture and arrangements allow ease of access.
Functional / Operational
Flexibility: The Conference/Classroom needs to be adaptable as occupant needs will change daily. These spaces generally will contain modular furniture that is light and easily rearranged. These spaces are generally located in areas with standard column grids and single story levels with flat floors. Movable partitions typically help to further subdivide the space as well as provide added projection surfaces. Design Conference/Classroom spaces that offer the potential for a wide range of interactions, from formal to informal, to inspire creative thinking and and engaged experience for participants. Also consider designing the Conference/Classroom space to allow for outdoor learning experiences if possible.
Special HVAC and Utility Requirements: A conference center will typically have a separate AHU, which requires a 15% increase in cooling capacity. HVAC, electrical, and security systems are generally designed to operate after hours on a regular basis. Toilet requirements are often exceeded to accommodate additional occupancy loads comfortably.
- Occupancy: Occupancy Group Classification is Business or Assembly A3, with sprinklered protected construction, and GSA Acoustical Class B1 space where meetings are held on a regular basis. See also WBDG Secure / Safe–Fire Protection.
Productive
Finishes and Built–In Conferencing Tools: These space types are generally finished with durable materials and surfaces that provide added conferencing and meeting functionality such as marker boards and projection screens. Ambient lighting with dimmable controls and special accent lighting is typically used to allow user control for presentation purposes. Consider energy–efficient lighting fixtures.
Integrated Technology: The Conference/Classroom is typically designed to accommodate a variety of audiovisual equipment, with special attention to acoustical separation from surrounding spaces.
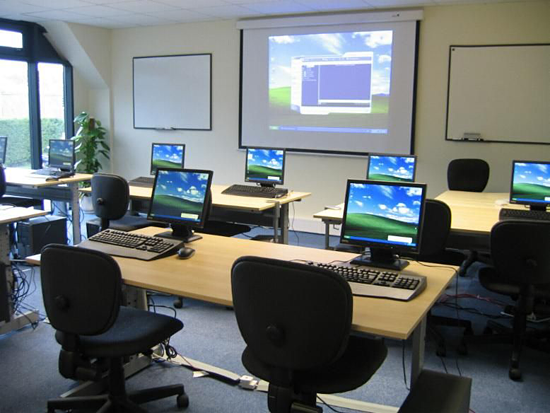

Plan for technology at individual learning stations as well as in the overall learning environment at optimal viewing locations.
Sustainable
- Provide excellent indoor air quality
- Provide natural daylighting and views to nature whenever possible
- Use energy efficient lighting
- Incorporate non-toxic materials, furnishings and finishes with low or no VOCs

A classroom at the Center for Sustainable Landscapes in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania has natural daylighting, natural ventilation, and healthy materials. For more information on this project, see the case study. Photo credit: Denmarsh Photography, Inc.
Example Program
The following building program is representative of Conference/Classroom space types.
CONFERENCE / CLASSROOM
| Description Tenant Occupiable Areas |
Qty. | SF Each | Space Req'd. | Sum Actual SF | Tenant Usable Factor | Tenant USF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Attendee Facilities | 1,190 | |||||
| Conference Reception | 1 | 400 | 400 | |||
| Coat Check | 1 | 60 | 60 | |||
| Attendee Toilets (Male) | 1 | 120 | 120 | |||
| Attendee Toilets (Female) | 1 | 160 | 160 | |||
| Break Lounge/Prefunction (capacity 15) |
2 | 225 | 450 | |||
| General Meeting | 6,380 | |||||
| Large Lecture (seating 120) | 2 | 1,200 | 2,400 | |||
| Multiple Purpose Meeting (seating 30) |
5 | 760 | 3,800 | |||
| Meeting Room Storage | 3 | 60 | 180 | |||
| Specialized Meeting Rooms | 1,350 | |||||
| Computer Training Lab (15 stations) |
2 | 675 | 1,350 | |||
| Tenant Suite | 8,920 | 1.20 | 10,661 | |||
| Tenant Usable Areas | 10,661 |
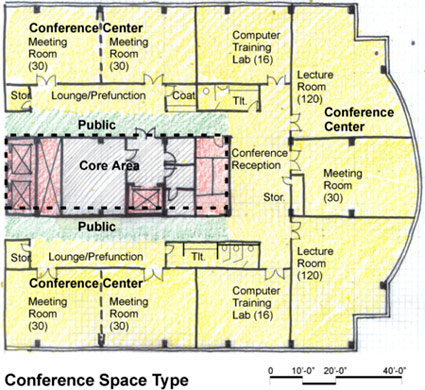
Example Plans
The following is representative of typical tenant plans.
Example Construction Criteria
For GSA, the unit costs for firing range space types are based on the construction quality and design features in the following tableDownload gsa_constr_criteria_conference.pdf . This information is based on GSA's benchmark interpretation and could be different for other owners.
Relevant Codes and Standards
The following agencies and organizations have developed codes and standards affecting the design of Conference/Classroom spaces. Note that the codes and standards are minimum requirements. Architects, engineers, and consultants should consider exceeding the applicable requirements whenever possible.
- ADA Standards for Accessible Design
- ICC IBC International Building Code
- PBS-P100 Facilities Standards for the Public Buildings Service, GSA
Additional Resources
Organizations and Associations
- U.S. Access Board
- Classroom Acoustics—A supplement to the ADA and ABA guidelines that addresses acoustics in classrooms.
Publications
- Accessible Information Exchange: Meeting on a Level Playing Field, by the U.S. Department of Justice, Civil Rights Division, Disability Rights Section.
- Architectural Graphic Standards, 12th Edition by The American Institute of Architects, Dennis J. Hall. New York, NY: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2016.










